What is the Middle Ear?
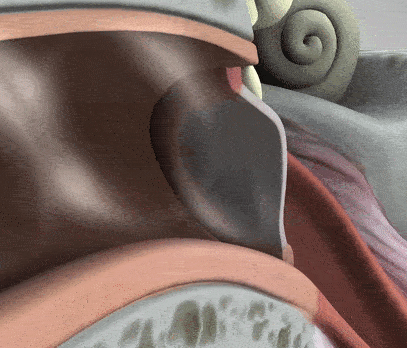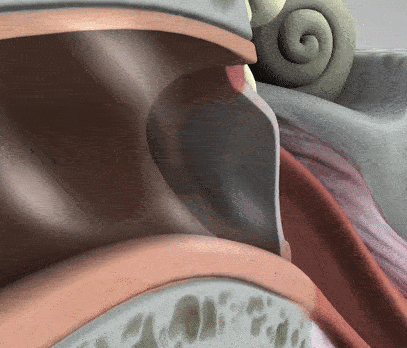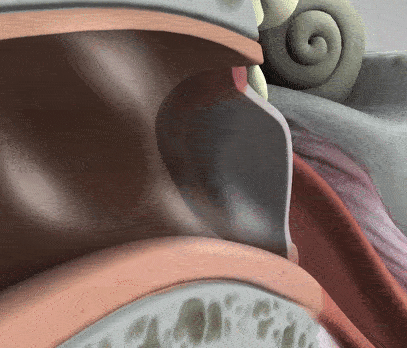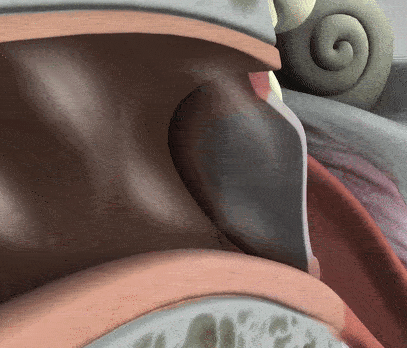 The middle ear is where the action really begins to take place with its unique structures, such as the tympanic membrane, the air-filled cavity, and the ossicular chain. The tympanic membrane, or eardrum as it is often referred to, is the first step in converting external sound waves into electrical signals in our brains. When sound strikes the tympanic membrane, it vibrates back and forth, transmitting the sound waves to the three small bones, the ossicles.
The middle ear is where the action really begins to take place with its unique structures, such as the tympanic membrane, the air-filled cavity, and the ossicular chain. The tympanic membrane, or eardrum as it is often referred to, is the first step in converting external sound waves into electrical signals in our brains. When sound strikes the tympanic membrane, it vibrates back and forth, transmitting the sound waves to the three small bones, the ossicles.
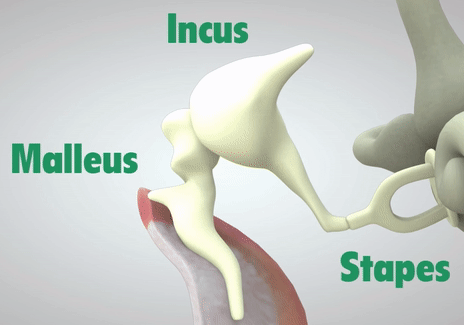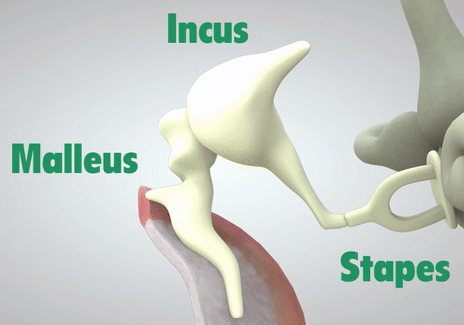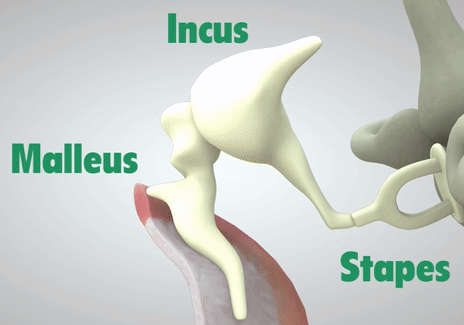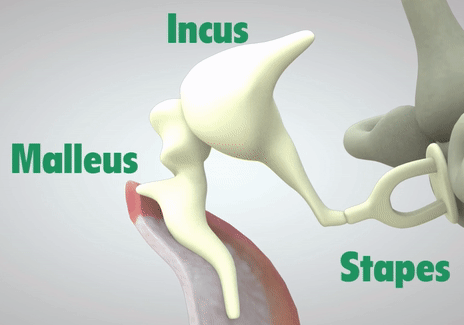 The ossicular chain is three small bones: the malleus, incus, and stapes (Humes & Bess, 2014). Moving from our eardrum to our inner ear, the malleus is first and is actually attachted to the eardrum. It moves alongside the vibrations of the eardrum. Then comes the incus, which helps connect the movement between the malleus and stapes. Lastly, connected to the incus, is the stapes. The stapes rests on a membrane, which is any barrier that allows what goes in and out. The membrane that the stapes sits on, the oval window, protects the inner ear from the workings of the middle ear and trasnmits sound from the ossicles to the inner ear.
The ossicular chain is three small bones: the malleus, incus, and stapes (Humes & Bess, 2014). Moving from our eardrum to our inner ear, the malleus is first and is actually attachted to the eardrum. It moves alongside the vibrations of the eardrum. Then comes the incus, which helps connect the movement between the malleus and stapes. Lastly, connected to the incus, is the stapes. The stapes rests on a membrane, which is any barrier that allows what goes in and out. The membrane that the stapes sits on, the oval window, protects the inner ear from the workings of the middle ear and trasnmits sound from the ossicles to the inner ear.
 There are two main muscles that help support the three ossicles: the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles. These two contract to reduce the intensity of sound transmission to the inner ear, further protection from the outer and middle ear to the inner ear. There is also the Eustachian tube, tubes that supply air to the middle ear cavity.
There are two main muscles that help support the three ossicles: the tensor tympani and stapedius muscles. These two contract to reduce the intensity of sound transmission to the inner ear, further protection from the outer and middle ear to the inner ear. There is also the Eustachian tube, tubes that supply air to the middle ear cavity. The tube remains closed, however, when one swallows or yawns, it opens, allowing air into the cavity, equalizing the air pressure of the eardrum on both sides. As you will see on the next page, the inner ear is sensitive and requires many pieces protective mechanisms to preserve its function.
The tube remains closed, however, when one swallows or yawns, it opens, allowing air into the cavity, equalizing the air pressure of the eardrum on both sides. As you will see on the next page, the inner ear is sensitive and requires many pieces protective mechanisms to preserve its function.
Pathology:
Acute otitis media (AOM) is a viral or bacterial infection that causes inflammation in the middle ear. It is very similar to otitis externa, but just occurs in a different part of the ear. AOM is one of the most common pediatric diagnoses, but it can occur at any age. AOM occurs in a few ways, but it often happens in children when the eustachian tube malfunctions and traps fluid in the middle ear, leading to the infection-prone environment.
 It can be diagnosed based on symptoms of inflammation and infection including swelling, redness, pus, and fluid in the middle ear. The assessment of AOM can be done using tympanometry, a hearing test, or reflectometry. AOM may resolve independently or through home care like applying warm moist cloth but if it persists, a medical professional often will prescribe antibiotics and possibly pain relievers. If treatment fails and infections are peristent, a doctor may recommend surgery to remove the adenoids to prevent earache, or suggest a myringotomy, the insertion of tiny tubes into the ear to relieve fluid buildup (Luo, 2019).
It can be diagnosed based on symptoms of inflammation and infection including swelling, redness, pus, and fluid in the middle ear. The assessment of AOM can be done using tympanometry, a hearing test, or reflectometry. AOM may resolve independently or through home care like applying warm moist cloth but if it persists, a medical professional often will prescribe antibiotics and possibly pain relievers. If treatment fails and infections are peristent, a doctor may recommend surgery to remove the adenoids to prevent earache, or suggest a myringotomy, the insertion of tiny tubes into the ear to relieve fluid buildup (Luo, 2019).